Cardiovascular and Endovascular
Biomedical textiles play a critical role in cardiovascular and endovascular applications, where they provide structural support, flexibility, and biocompatibility for devices used in life-saving procedures.
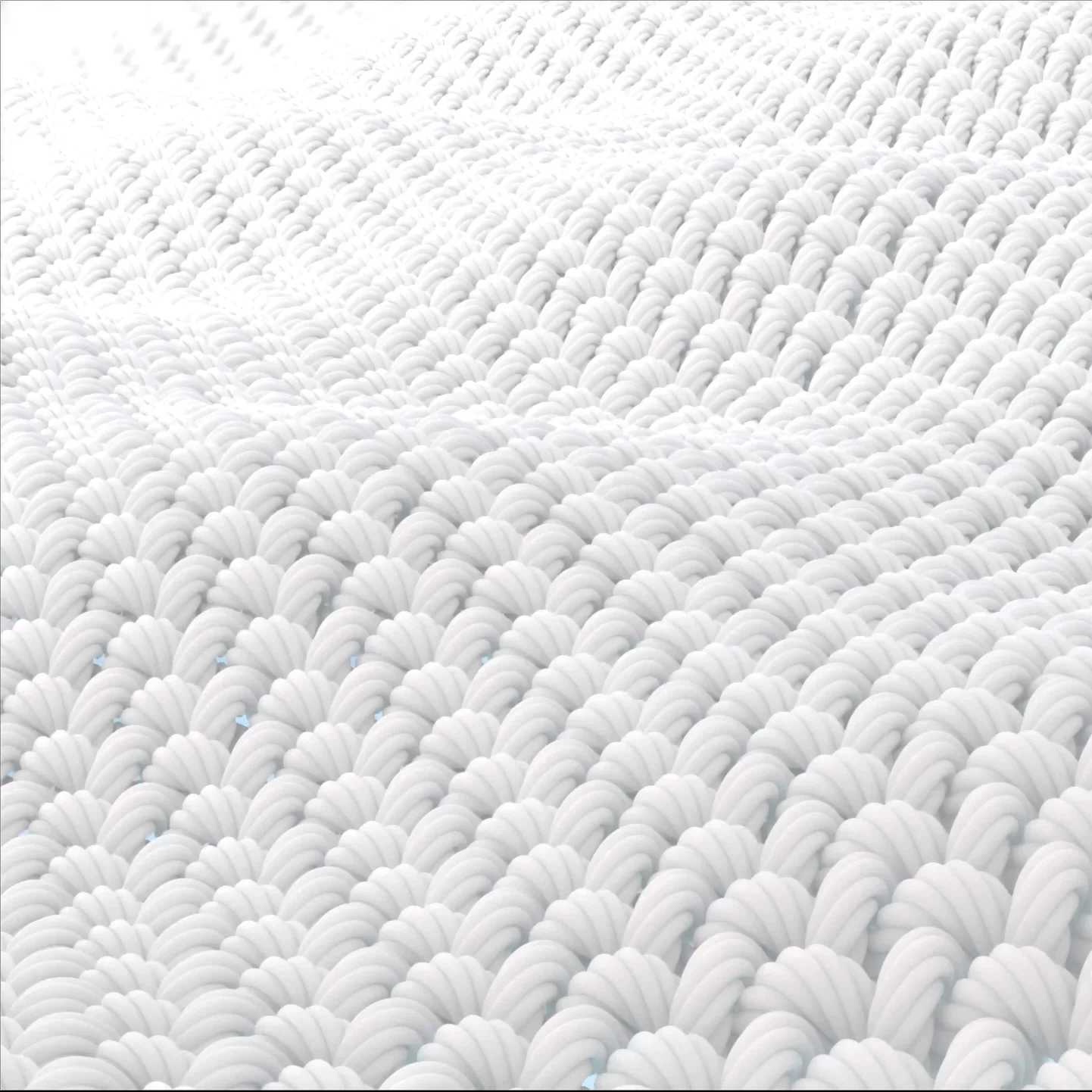
These textiles are designed with advanced engineering techniques like knitting, braiding, and weaving, using medical-grade fibres that offer the required mechanical properties and long-term biocompatibility.
Biomedical textiles play a critical role in cardiovascular and endovascular applications, where they provide structural support, flexibility, and biocompatibility for devices used in life-saving procedures.
These textiles are designed with advanced engineering techniques like knitting, braiding, and weaving, using medical-grade fibres that offer the required mechanical properties and long-term biocompatibility.
Key Biomedical Textile Solutions for Cardiovascular and Endovascular Applications
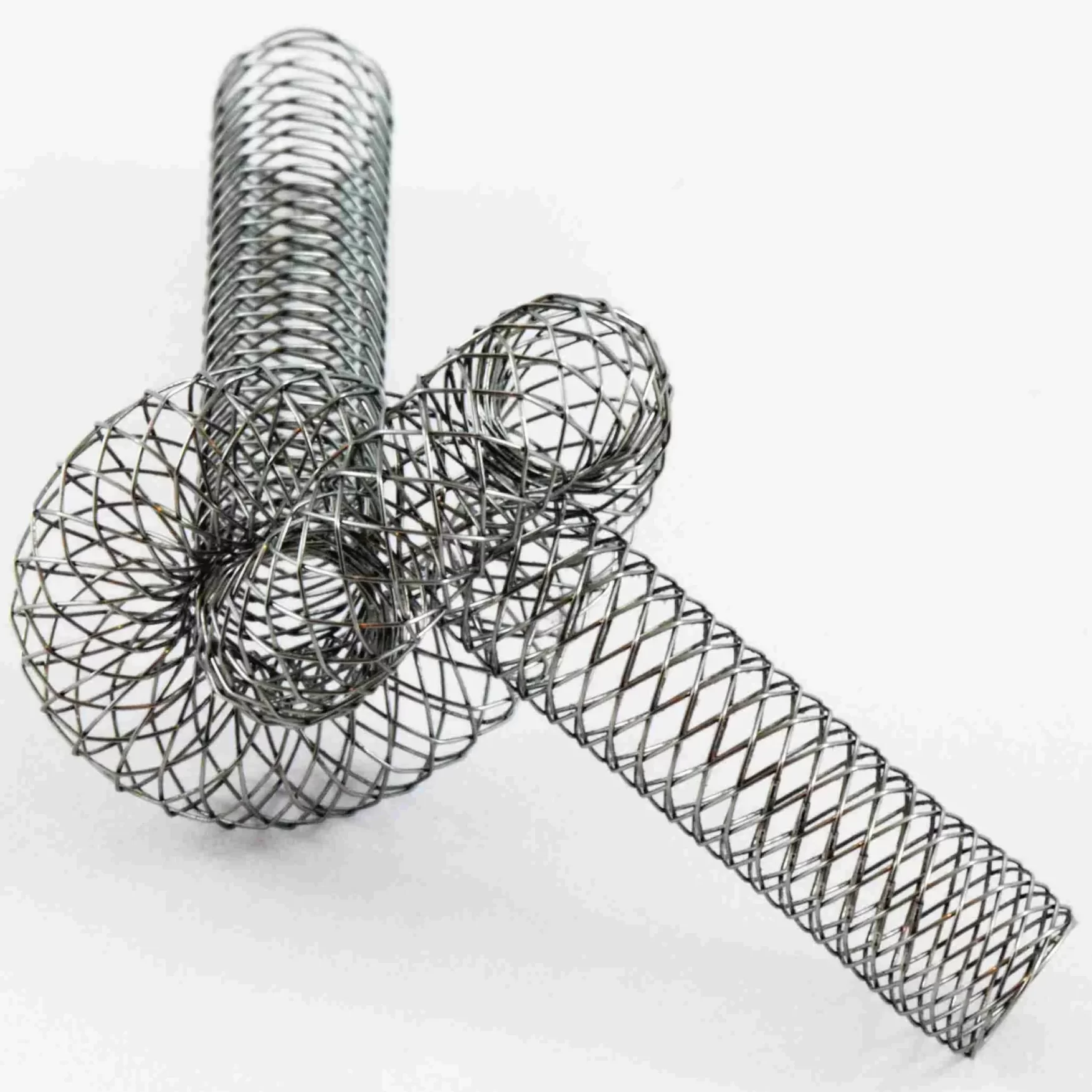
Vascular Grafts and Stent Grafts
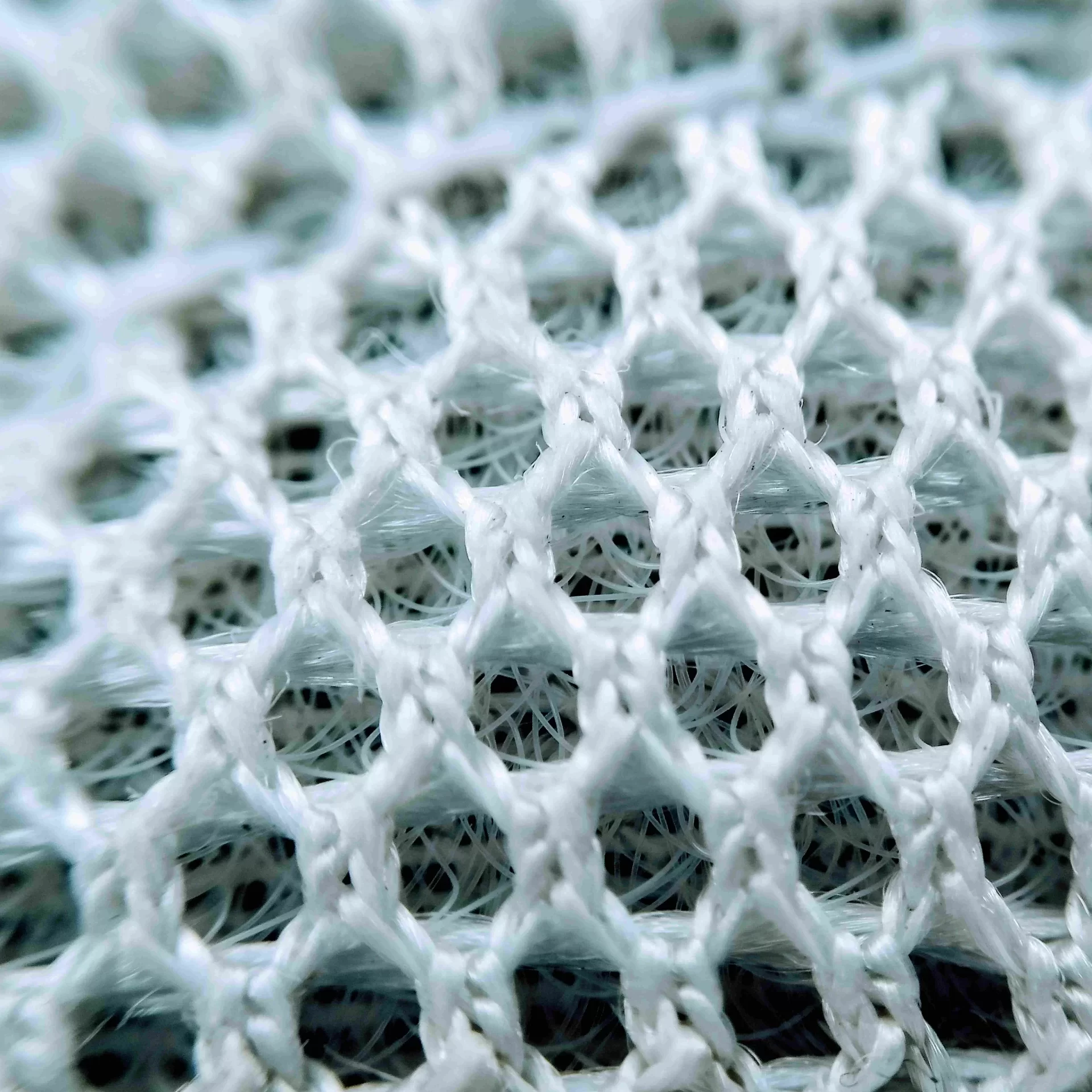
Knitted or woven fabrics: Used to replace or repair damaged blood vessels. They offer strength, compliance, and the ability to allow tissue in-growth for better integration with the body.
Bifurcated grafts: Commonly used for aortic aneurysms, they are designed for anatomical precision.
Materials: ePTFE (expanded polytetrafluoroethylene), Dacron (polyester), and other polymeric fibres that provide long-term durability and stability.
Endovascular Stents and Stent Grafts
Textile components are integrated into stents to provide a flexible and secure fit within blood vessels.
Braided stent grafts: Offer radial strength and flexibility, important for navigating tortuous vascular pathways.
Materials: Nitinol (nickel-titanium alloy), synthetic fibres like polyester or polyurethane, for high fatigue resistance.
Heart Valve Sewing Rings
Knitted or woven textile sewing rings are used to secure replacement heart valves. These textiles need to exhibit both biocompatibility and hemocompatibility, ensuring no adverse reactions with blood while offering reliable suture retention.
Materials: Polyester
Embolic Protection Devices
These devices use fine-mesh textiles to filter or capture embolic debris during cardiovascular procedures like stenting.
Textiles used are often braided for flexibility and strength, maintaining blood flow while trapping particles.
Materials: Ultra-thin polymeric fibres, often coated with heparin or other agents to prevent clotting.
Occlusion Devices
Textiles are key in occlusion devices used to close defects or aneurysms in blood vessels or the heart. They must conform well to anatomical structures while creating a secure closure.
Materials: Biocompatible polymers like PET (polyethylene terephthalate)
Vascular Patches
Used to repair damaged blood vessels or reinforce arterial walls, these patches must maintain compliance and burst strength.
Materials: Polyester, PTFE.
Key Biomedical Textile Solutions for
Cardiovascular and Endovascular Applications
Key Biomedical Textile Solutions for Cardiovascular and Endovascular Applications
Vascular Grafts and Stent Grafts
Knitted or woven fabrics: Used to replace or repair damaged blood vessels. They offer strength, compliance, and the ability to allow tissue in-growth for better integration with the body.
Bifurcated grafts: Commonly used for aortic aneurysms, they are designed for anatomical precision.
Materials: ePTFE (expanded polytetrafluoroethylene), Dacron (polyester), and other polymeric fibres that provide long-term durability and stability.
Endovascular Stents and Stent Grafts
Textile components are integrated into stents to provide a flexible and secure fit within blood vessels.
Braided stent grafts: Offer radial strength and flexibility, important for navigating tortuous vascular pathways.
Materials: Nitinol (nickel-titanium alloy), synthetic fibres like polyester or polyurethane, for high fatigue resistance.
Heart Valve Sewing Rings
Knitted or woven textile sewing rings are used to secure replacement heart valves. These textiles need to exhibit both biocompatibility and hemocompatibility, ensuring no adverse reactions with blood while offering reliable suture retention.
Materials: Polyester
Embolic Protection Devices
These devices use fine-mesh textiles to filter or capture embolic debris during cardiovascular procedures like stenting.
Textiles used are often braided for flexibility and strength, maintaining blood flow while trapping particles.
Materials: Ultra-thin polymeric fibres, often coated with heparin or other agents to prevent clotting.
Occlusion Devices
Textiles are key in occlusion devices used to close defects or aneurysms in blood vessels or the heart. They must conform well to anatomical structures while creating a secure closure.
Materials: Biocompatible polymers like PET (polyethylene terephthalate).
Vascular Patches
Used to repair damaged blood vessels or reinforce arterial walls, these patches must maintain compliance and burst strength.
Materials: Polyester, PTFE.
Manufacturing Techniques
Manufacturing Techniques
These custom-designed textile solutions help medical devices improve outcomes in cardiovascular surgery, minimally invasive procedures, and long-term implants.TEXMEDIX’s expertise in advanced textile fabrication techniques positions it well to innovate in this field.